Material Hardness Instruments Buying Guide
Maintaining the integrity of your materials is crucial across various industries. Material hardness is a key indicator of durability, wear resistance, and overall performance. Here at BlastOne, we understand the importance of selecting the appropriate hardness tester for your specific needs.
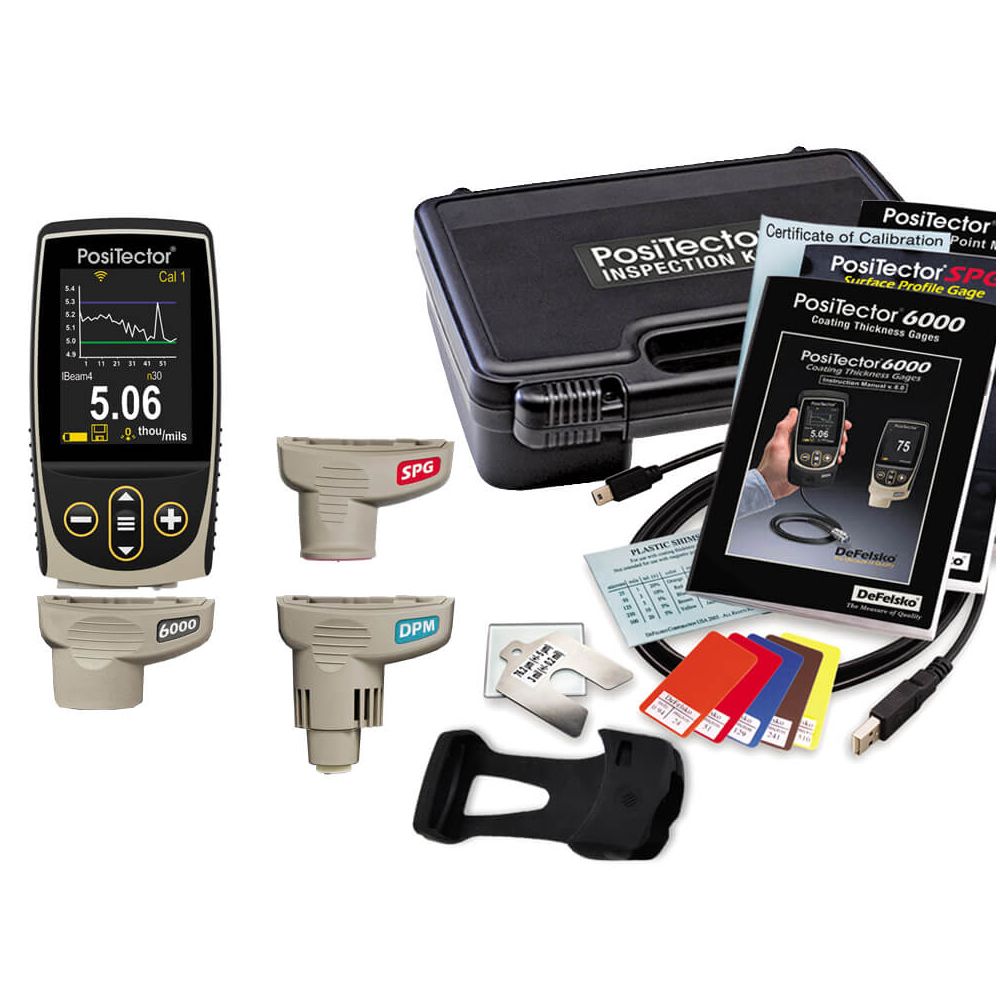
We offer a comprehensive range of DeFelsko hardness testers, each designed to excel in different applications. Whether you’re working with soft rubbers, hard plastics, or evaluating the scratch resistance of coatings, BlastOne has the right tool to ensure accurate and reliable hardness measurements.
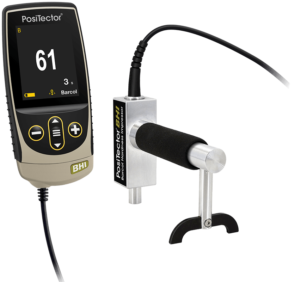
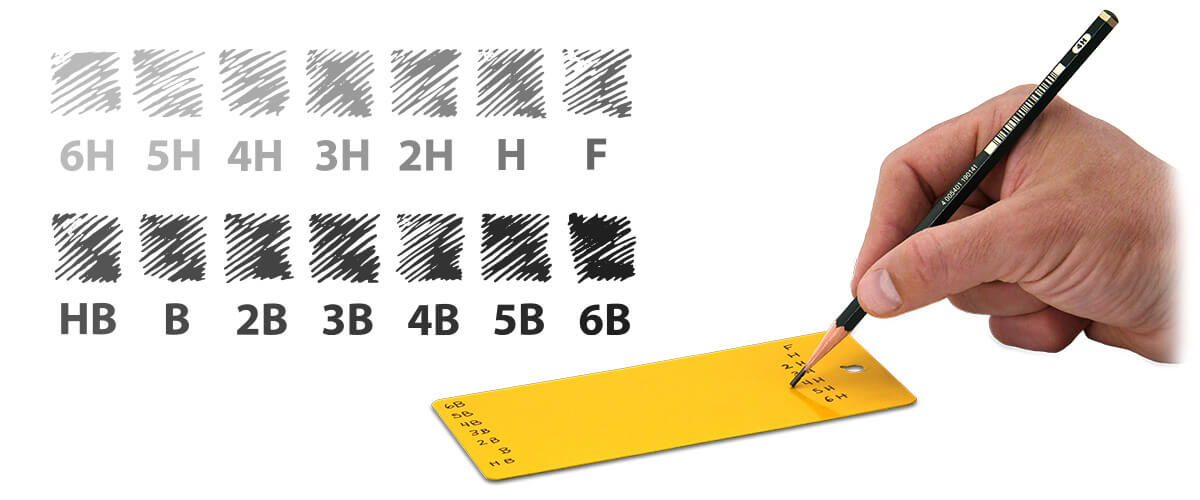
Our PosiTector lineup features user-friendly digital models for efficient data collection and standardized testing in accordance with recognized industry standards. Keep reading to delve into the strengths and limitations of each PosiTector model (SHD, BHI, PT) and discover the perfect hardness tester for your quality control or material assessment tasks.
 My Account
My Account