Holiday Detector Instruments Buying Guide
Ensuring a flawless finish is crucial for long-lasting corrosion protection. Pinhole and holiday detectors, also known as porosity testers or spark testers, are vital tools to identify defects in your coating system. Small areas of thin or missing coating, known as pinholes or holidays, can act as gateways for corrosion. These imperfections significantly shorten the lifespan of your protective coating system.
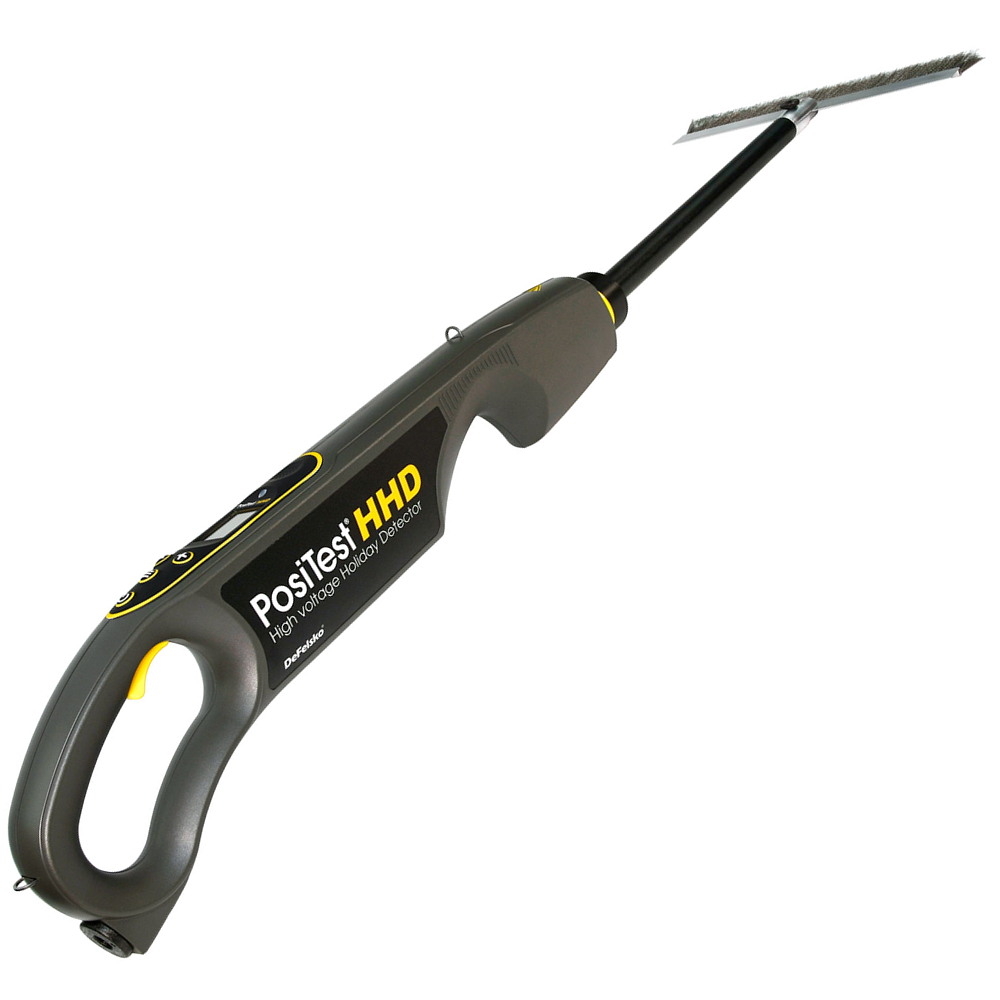
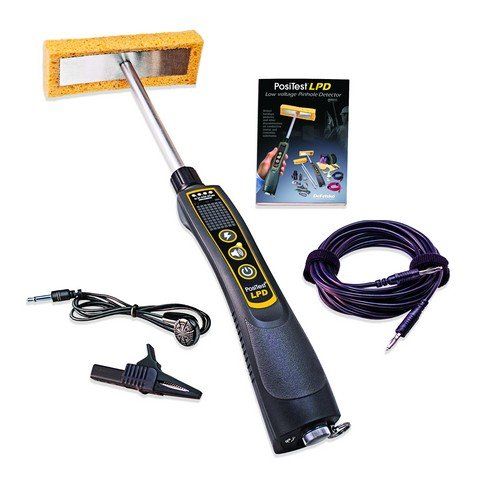
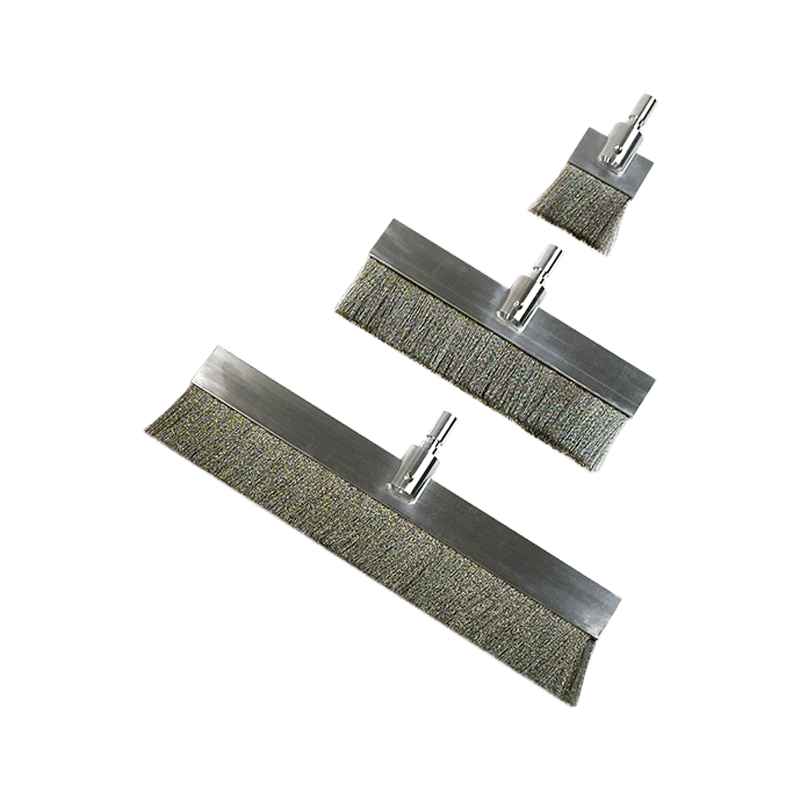
BlastOne offers two types of pinhole detectors: low voltage (wet sponge tester) and high voltage (spark tester). Low voltage detectors, like the PosiTest LPD, are typically used on paint systems less than 500 µm (20 mils) thick. High voltage holiday testers, like the PosiTest HHD operate at voltages up to 35,000 V and are typically used on coatings at least 200 µm (8 mils) thick.
This guide explores pinhole and holiday detectors, also known as porosity testers or spark testers, which are non-destructive tools that help identify these defects before corrosion sets in.
 My Account
My Account